
rocket domain was triggered too early. This is usually an indicator for some code in the plugin or theme running too early. Translations should be loaded at the init action or later. Please see Debugging in WordPress for more information. (This message was added in version 6.7.0.) in /var/www/rahi_io/wp-includes/functions.php on line 6114

The increasing adoption of advanced cloud computing technologies such as AI, IoT, machine learning, and big data has driven the market size for Infrastructure As A Service (IaaS). According to Fortune Business Insights, the market size is expected to grow from $130.08 billion in 2023 to $531.84 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 22.3%. IaaS play a pivotal role in providing organizations with the flexibility and agility they need to thrive in a dynamic marketplace.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding IaaS, its benefits, and its role in the realm of cloud infrastructure solutions.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that offers virtualized computing resources over the internet. The cloud provider manages IT structures (servers, storage, networks, virtualization, etc.) for organizations on a subscription basis over the Internet. Organizations can access essential IT infrastructure components without having to invest in physical hardware or maintain complex data centers. The IaaS is usually the next step organizations take from on-premises.
The agility and flexibility that comes from IaaS is an advantage. Organizations are able to bring additional hardware resources online on-demand, and pay only for the resources consumed making it easier to adapt to seasonal spikes in demand or unusually low business. The distributed resources of your cloud provider can be utilized in countries or regions where there is consumption. This results in lower latency, improved efficiency and better overall performance. The additional advantage is being able to conform with local regulations.
In the era of cloud computing, cloud infrastructure solutions, particularly Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), have emerged as crucial enablers for organizations seeking scalable, cost-efficient, and flexible IT infrastructure solutions.
The trend in maintaining a mobile workforce enables employees to access data over the internet anywhere they are without compromising security. The developing trend of digitization is one of the key factors driving the growth of IaaS.
As cloud infrastructure solutions continue to evolve, organizations must assess their specific needs and choose a reliable provider that aligns with their goals and requirements. Embracing IaaS is not just a technological choice; it is a strategic move towards a more efficient and adaptive future.

Rahi is an independently operated subsidiary of Wesco Distribution, Inc. Wesco is a Fortune 200 Company with Annual Revenues of more than USD $19B, 19,000+ Employees, and operates in 50+ countries globally. Rahi was acquired by Wesco in November of 2022. With warehouses and offices in 50+ countries, Rahi offers the advantage of IOR services, local currency billing, and RMA services - helping businesses operate efficiently and successfully at any location. Rahi combines its global reach and in-depth analysis services to understand clients’ business goals, IT requirements, and operations while placing them on the journey toward success.

Technology has integrated every aspect of business operations. Even a few seconds of downtime can result in...

The increasing expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), the rise of cloud computing and software-as-a-service...
Data centers are critical to the digital world, powering everything from social media platforms and streaming services...

In an era where digital transformation is reshaping businesses, the uptime of data center services has become a...

Today, our lives are dependent on technology and the services data centers provide. As more and more businesses...

In a world that is only always “on”, high costs are associated with downtime. According to a Poneman Institute...

With more organizations digitizing their operations, the volume of data that organizations are seeking to manage is...

Data centers are the engines powering the rapidly growing information economy. In today’s digital world, the demand...

In the digital age, the way we communicate and collaborate has changed dramatically. As we’ve shifted towards a...

In the era of digital transformation, Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to push the boundaries of what is...

In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the way businesses communicate and collaborate has undergone...

In our interconnected world, data centers play a vital role, acting as the backbone of our digital infrastructure. As...

In the universe of coding, even the most seasoned developers sometimes find themselves seeking guidance or hunting for...

As companies embrace the digital age, reliable and efficient network operation has become essential. To that end,...
Technology advancements have forced organizations to adopt technologies into their operations. In the digital age,...

Are your IT personnel able to keep up with the rapidly evolving digital age, maintaining optimal network performance...

Innovations in technology have opened up a host of opportunities for organizations to streamline their operations and...

In today’s technology evolved society, customers expect the same efficiency and speed from small businesses as they...

Having a reliable and secure IT infrastructure is no longer a nice-to-have option for growing businesses. In a digital...
The advancement of technology and the need for digital transformation have led many organizations to adopt a...
A resilient business can be defined as one that can bounce back from any kind of setback with minimal downtime. In...

Technology is no longer a nice-to-have option for businesses. It can be the difference between a successful business...

In today’s digital-driven business landscape, network uptime is no longer just a nice-to-have; it’s a...

A Networks Operation Center (NOC) is the first line of defence against network interruptions, and failures. With most...

In an increasingly digital world, the specter of cyber threats looms large. From large corporations to small...

In the digital age, data centers have become the backbone of businesses, housing critical infrastructure that keeps...
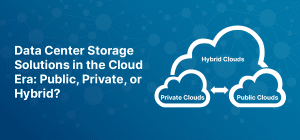
In the digital age, Data Center Storage Solutions are rapidly evolving. The advent of cloud computing has led to a...

The advent of the digital age has brought about an exponential growth in data generation. As businesses transition...

Introduction: Zoom has become an essential tool in today’s digitally driven world, enabling seamless remote...

Introduction: As the world embraces remote work and virtual meetings, Zoom has become an essential tool for...

The digital revolution is upon us. The insatiable demand for data has driven a meteoric rise in the number of data...

As a company specializing in high-performance data center solutions, we at Rahi Systems understand the importance of...

In an era where technology advancements are taking giant leaps forward, staying updated and connected with the latest...

As a technology enthusiast, you are likely always on the hunt for the next ground-breaking innovation, the latest...

Cloud technology is a great indicator of how the world is progressing and how organizations are using the cloud to...

Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a suite of cloud computing services that offer hosting on the same supporting...

In an increasingly digital age, the importance of data centers in storing, managing, and disseminating data cannot be...

Countless data centers power our digital world supporting billions of digital processes every day. It’s easy to...

Seamless communication and collaboration are driving boardroom efficiency enabling directors to collaborate actively...

The global Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) market size is expected grow at a CAGR of nearly 16% from 2023...

The safety and security of data centers have never been more critical than in the current hyper-connected digital...

As businesses increasingly rely on digital infrastructure to operate, the need for reliable and secure data centers...
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has taken center stage and the massive adoption of AI has disrupted businesses across...

In the digital era, the shift to cloud-based infrastructure has become not just a trend, but a business necessity. A...

As organizations increasingly adopt cloud-based infrastructure, ensuring cloud migration security has become a...

In today’s digital age, businesses are increasingly recognizing the need to modernize their IT infrastructure ...

Hybrid cloud adoption represents the fusion of private and public cloud resources, creating an integrated, flexible,...

Cloud-computing has been a disruptive game-changer for organizations forcing organizations to digitally transform. The...

Clouds have evolved. With the proliferation of big data, clouds have developed from being platforms used for merely...
The digital era is here. Organizations are adopting hybrid multi-cloud systems that offer several advantages such as...

In recent years, Software-Defined Data Centers (SDDC) have gained significant traction as a next-generation data...

The primary benefit of data center cooling units is temperature regulation. Maintaining an optimal temperature range...

Cloud computing has experienced a dramatic acceleration becoming an essential catalyst for businesses looking for...

As organizations increase their dependence on technology, there are a host of new challenges that arise such as...

In today’s digital age, almost every sector relies on private and public cloud computing technologies to operate...

As technology advances, the need for more storage of digital data has grown exponentially. Network-attached storage...

The accumulation of massive data has spiked the need for efficient and cost-effective data management solutions. Data...

In today’s world, cellular networks have become an essential part of our daily lives. However, the cost of using...

As the world becomes increasingly connected, the importance of fast and reliable network connections has grown...

Managed services are an increasingly popular approach to IT infrastructure management and support. As businesses...

A Managed Services Model is a way of outsourcing IT management and support services to a third-party provider. This...

Data centers are integral parts of the modern digital world, providing storage and processing power for a vast array...

As businesses increasingly rely on technology, managing IT operations can be a challenge. A Managed Services Model for...

As businesses increasingly rely on technology, managing IT operations can be a challenge. A Managed Services Model...

Data centers are integral parts of the modern digital world, providing storage and processing power for a vast...

A Managed Services Model is a way of outsourcing IT management and support services to a third-party provider. This...

Managed services are an increasingly popular approach to IT infrastructure management and support. As businesses...
As the world becomes increasingly connected, the importance of fast and reliable network connections has grown...

In today's world, cellular networks have become an essential part of our daily lives. However, the cost of using...

Cyber threats are continually on the rise and many businesses do not have the resources to monitor and manage such...

Technology is accelerating at an amazing pace. Organizations need to keep up with IT infrastructures that are...

Data center extension has been gaining momentum in businesses wanting to leverage the cloud’s elasticity and...

As businesses grow, so does their need for reliable and scalable data center infrastructure. Scaling IT ecosystems...

The accumulation of massive data has spiked the need for efficient and cost-effective data management solutions....

As technology advances, the need for more storage of digital data has grown exponentially. Network-attached storage...

In today's digital age, almost every sector relies on private and public cloud computing technologies to operate...
As organizations increase their dependence on technology, there are a host of new challenges that arise such as...

Cloud computing has experienced a dramatic acceleration becoming an essential catalyst for businesses looking for...

The primary benefit of data center cooling units is temperature regulation. Maintaining an optimal temperature...
In recent years, Software-Defined Data Centers (SDDC) have gained significant traction as a next-generation data...
The digital era is here. Organizations are adopting hybrid multi-cloud systems that offer several advantages such...
Clouds have evolved. With the proliferation of big data, clouds have developed from being platforms used for merely...
Cloud-computing has been a disruptive game-changer for organizations forcing organizations to digitally transform....

Hybrid cloud adoption represents the fusion of private and public cloud resources, creating an integrated,...

In today's digital age, businesses are increasingly recognizing the need to modernize their IT infrastructure to...

As organizations increasingly adopt cloud-based infrastructure, ensuring cloud migration security has become a...

In the digital era, the shift to cloud-based infrastructure has become not just a trend, but a business necessity....
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has taken center stage and the massive adoption of AI has disrupted businesses across...

As businesses increasingly rely on digital infrastructure to operate, the need for reliable and secure data centers...

The safety and security of data centers have never been more critical than in the current hyper-connected digital...

The global Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) market size is expected grow at a CAGR of nearly 16% from...

Seamless communication and collaboration are driving boardroom efficiency enabling directors to collaborate...

Countless data centers power our digital world supporting billions of digital processes every day. It's easy to...
In an increasingly digital age, the importance of data centers in storing, managing, and disseminating data cannot...
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is a suite of cloud computing services that offer hosting on the same supporting...
Cloud technology is a great indicator of how the world is progressing and how organizations are using the cloud to...

As a technology enthusiast, you are likely always on the hunt for the next ground-breaking innovation, the latest...

In an era where technology advancements are taking giant leaps forward, staying updated and connected with the...

As a company specializing in high-performance data center solutions, we at Rahi Systems understand the importance...
The digital revolution is upon us. The insatiable demand for data has driven a meteoric rise in the number of data...

Introduction: As the world embraces remote work and virtual meetings, Zoom has become an essential tool for...

Introduction: Zoom has become an essential tool in today's digitally driven world, enabling seamless remote...
The advent of the digital age has brought about an exponential growth in data generation. As businesses transition...
In the digital age, Data Center Storage Solutions are rapidly evolving. The advent of cloud computing has led to a...
In the digital age, data centers have become the backbone of businesses, housing critical infrastructure that keeps...
In an increasingly digital world, the specter of cyber threats looms large. From large corporations to small...

A Networks Operation Center (NOC) is the first line of defence against network interruptions, and failures. With...
In today's digital-driven business landscape, network uptime is no longer just a nice-to-have; it's a must-have. A...

Technology is no longer a nice-to-have option for businesses. It can be the difference between a successful...
A resilient business can be defined as one that can bounce back from any kind of setback with minimal downtime. In...
The advancement of technology and the need for digital transformation have led many organizations to adopt a...

Having a reliable and secure IT infrastructure is no longer a nice-to-have option for growing businesses. In a...
In today’s technology evolved society, customers expect the same efficiency and speed from small businesses as...

Innovations in technology have opened up a host of opportunities for organizations to streamline their operations...

Are your IT personnel able to keep up with the rapidly evolving digital age, maintaining optimal network...
Technology advancements have forced organizations to adopt technologies into their operations. In the digital age,...

As companies embrace the digital age, reliable and efficient network operation has become essential. To that end,...

In the universe of coding, even the most seasoned developers sometimes find themselves seeking guidance or hunting...

In our interconnected world, data centers play a vital role, acting as the backbone of our digital infrastructure....

In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, the way businesses communicate and collaborate has undergone...
In the era of digital transformation, Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to push the boundaries of what is...
In the digital age, the way we communicate and collaborate has changed dramatically. As we've shifted towards a...
Data centers are the engines powering the rapidly growing information economy. In today’s digital world, the...

With more organizations digitizing their operations, the volume of data that organizations are seeking to manage is...

In a world that is only always “on”, high costs are associated with downtime. According to a Poneman Institute...

Today, our lives are dependent on technology and the services data centers provide. As more and more businesses...

In an era where digital transformation is reshaping businesses, the uptime of data center services has become a...
Data centers are critical to the digital world, powering everything from social media platforms and streaming...

The increasing expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT), the rise of cloud computing and software-as-a-service...
Technology has integrated every aspect of business operations. Even a few seconds of downtime can result in...
Let our experts design, develop, deploy and manage your requirements while you focus on what's important for your business
Please check your inbox for more details.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |